一、本期重点:
1、基于双曲超材料的极度灵敏传感平台
Extreme sensitivity biosensing platform based on hyperbolic metamaterials
DOI: 10.1038/NMAT4609
PUBLISHED ONLINE: 28 MARCH 2016
内容介绍:
在医疗研究和临床诊断领域,光学生物传感技术提供了重要的发展契机,特别,将这种传感技术应用于检测稀溶液中小分子量的生物化学分子,已经成为研究的热点。虽然包括基于超材料的免标记等离子生物传感等一些研究的方法已经被用于这种研究的方式,然而,由于小分子极低的电子极化性,这种对于在稀溶液中低于分子量(<500 Da)生物分子的检测仍然是一个巨大的挑战。
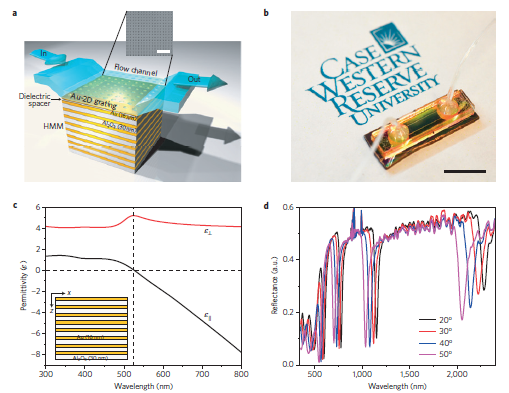
图a图b是双曲超材料平台基本机构图,包括微流通芯片双曲超材料以及二维光栅结构。
图c表征了双曲超材料的基本结构,并且绘制了介电张量的水平和垂直的色散曲线.
图d表征了进行芯片标定的光谱响应图谱,显示了不同模式的光谱响应。
2、Enhancing the Angular Sensitivity of Plasmonic Sensors Using Hyperbolic Metamaterials
运用双曲超材料的增强角度灵敏度的等离子传感器
【Adv. Optical Mater】
DOI: 10.1002/adom.201600448
Published:2016.07.01
内容简介:
SPR工作方式分为两种,一种是棱镜耦合型,一种是光栅耦合型。.现在调制类型主要以光谱波长调制和角度调制。角度调制类型由于是单波长,信噪比特别低,一般的角度调制性SPR灵敏度在为500-600度/RIU。棱镜耦合型由于其整体器件,终究是大体积的终端仪器,不符合小型化要求。先进的光刻技术用于加工亚波长的光栅结构是该文文章的技术亮点。光栅耦合型的SPR仪器,可以小型化,满足芯片实验室未来趋势的要求,例如,抗原抗体,蛋白质,化学检测。光栅耦合类型的角度调制性SPR主要挑战在于,入射波长,棱镜材料,衍射序列。文章将亚波长衍射光栅和双曲超材料结合设计一种等离子传感器。本文属于平板的一维双曲超材料。双曲超材料是各向异性的介电常数材料。双曲超材料支持高k模式,并且具有自发发射增强,纳米成像,负折射和完美吸收的应用潜力。检测低于500Da分子量的生物应用主要是为了现在为满足的临床需求,因为现在检测一些癌症细胞在现在可见光医学传感技术下难以检测,比如CPMV。该文中提到的双曲超材料由Al2O3和Au层层堆叠而成,Al2O3为电子书蒸镀方法,Au为热蒸镀而成,相互堆叠16层。
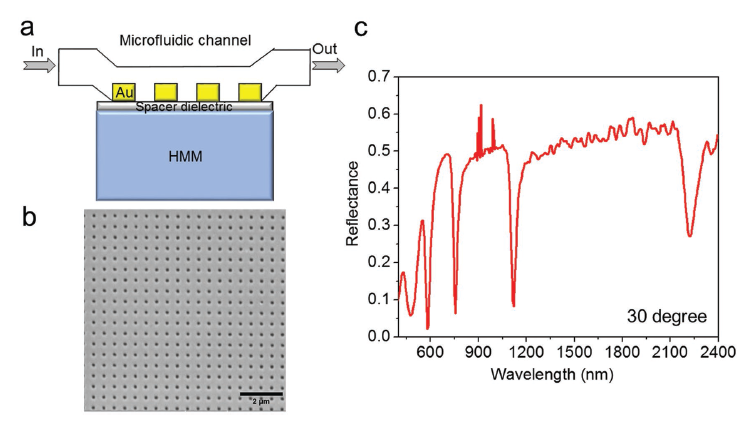
图a为角度调制型双曲超材料结构等离子生物传感器的基本机构图示。图b为所加工的二维光栅结构的SEM图示。图c是应用该双曲超材料超灵敏传感器的光谱响应,图中显示,该光谱响应具有多种响应模式。
二、简讯:
1、Label-free SPR detection of gluten peptides in urine for non-invasive celiac disease follow-up
尿液中蛋白水解多肽非侵入性的腹腔疾病追踪的无标记的SPR检测
【Biosensors & Bioelectronics】
DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.11.097
Published:2016.06.05
Abstract:
Motivated by the necessity of new and efficient methods for dietary gluten control of celiac patients, we have developed a simple and highly sensitive SPR biosensor for the detection of gluten peptides in urine. The sensing methodology enables rapid and label-free quantification of the gluten immunogenic peptides (GIP) by using G12 mAb. The overall performance of the biosensor has been in-depth optimized and evaluated in terms of sensitivity, selectivity and reproducibility, reaching a limit of detection of 0.33ngmL(-1). Besides, the robustness and stability of the methodology permit the continuous use of the biosensor for more than 100 cycles with excellent repeatability. Special efforts have been focused on preventing and minimizing possible interferences coming from urine matrix enabling a direct analysis in this fluid without requiring extraction or purification procedures. Our SPR biosensor has proven to detect and identify gluten consumption by evaluating urine samples from healthy and celiac individuals with different dietary gluten conditions. This novel biosensor methodology represents a novel approach to quantify the digested gluten peptides in human urine with outstanding sensitivity in a rapid and non-invasive manner. Our technique should be considered as a promising opportunity to develop Point-of-Care (POC) devices for an efficient, simple and accurate gluten free diet (GFD) monitoring as well as therapy follow-up of celiac disease patients.
2、3D plasmonic crystal metamaterials for ultra-sensitive biosensing
三维等离子晶体材料的超灵敏生物传感
【Scientific Reports】
doi:10.1038/srep25380
Published online: 2016.05.06
Abstract:
We explore the excitation of plasmons in 3D plasmon crystal metamaterials and report the observation of a delocalized plasmon mode, which provides extremely high spectral sensitivity (>2600 nm per refractive index unit (RIU) change), outperforming all plasmonic counterparts excited in 2D nanoscale geometries, as well as a prominent phase-sensitive response (>3*104 deg. Of phase per RIU). Combined with a large surface for bioimmobilization provided by the 3D matrix, the proposed sensor architecture promises a new important landmark in the advancement of plasmonic biosensing technology.
3、High-Throughput Fabrication of Resonant Metamaterials with Ultrasmall Coaxial Apertures via Atomic Layer Lithography
超小型同轴孔通过原子层光刻谐振材料的高通量制备
【nano letters】
DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00024
Published : 2016.02.16
Abstract:
We combine atomic layer lithography and glancing-angle ion polishing to create wafer-scale metamaterials composed of dense arrays of ultrasmall coaxial nanocavities in gold films. This new fabrication scheme makes it possible to shrink the diameter and increase the packing density of 2 nm-gap coaxial resonators, an extreme subwavelength structure first manufactured via atomic layer lithography, both by a factor of 100 with respect to previous studies. We demonstrate that the nonpropagating zeroth-order Fabry-Pérot mode, which possesses slow light-like properties at the cutoff resonance, traps infrared light inside 2 nm gaps (gap volume ∼ λ3/106). Notably, the annular gaps cover only 3% or less of the metal surface, while open-area normalized transmission is as high as 1700% at the epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) condition. The resulting energy accumulation alongside extraordinary optical transmission can benefit applications in nonlinear optics, optical trapping, and surface-enhanced spectroscopies. Furthermore, because the resonance wavelength is independent of the cavity length and dramatically red shifts as the gap size is reduced, large-area arrays can be constructed with λresonance ≫ period, making this fabrication method ideal for manufacturing resonant metamaterials.
4、Infrared Plasmonic Refractive Index Sensor with Ultra-High Figure of Merit Based on the Optimized All-Metal Grating
基于优化全金属光栅的超高品质因子等离子体折射率传感器
【Nanoscale Research Letters】
DOI: 10.1186/s11671-016-1773-2
Published : 2016.11.09
Abstract:
A perfect ultra-narrow band infrared metamaterial absorber based on the all-metal-grating structure is proposed. The absorber presents a perfect absorption efficiency of over 98% with an ultra-narrow bandwidth of 0.66 nm at normal incidence. This high efficient absorption is contributed to the surface plasmon resonance. Moreover, the surface plasmon resonance-induced strong surface electric field enhancement is favorable for application in biosensing system. When operated as a plasmonic refractive index sensor, the ultra-narrow band absorber has a wavelength sensitivity 2400 nm/RIU and an ultra-high figure of merit 3640, which are much better than those of most reported similar plasmonic sensors. Besides, we also comprehensively investigate the influences of structural parameters on the sensing properties. Due to the simplicity of its geometry structure and its easiness to be fabricated, the proposed high figure of merit and sensitivity sensor indicates a competitive candidate for applications in sensing or detecting fields.
供稿:孙毅







