一、本期重点:
1、用于提高熔石英光学元件表面激光损伤阈值的反应离子刻蚀处理(Reaction ion etching process for improving laser damage resistance of fused silica optical surface)【OPTICS EXPRESS】
DOI: 10.1364/OE.24.000199
Published:2016/1/5
1、用于提高熔石英光学元件表面激光损伤阈值的反应离子刻蚀处理(Reaction ion etching process for improving laser damage resistance of fused silica optical surface)【OPTICS EXPRESS】
DOI: 10.1364/OE.24.000199
Published:2016/1/5
在抛光、研磨工艺过程中,熔石英光学元件表面及亚表面将会产生各种缺陷,而激光损伤主要发生在这些缺陷处,学者们研究探讨了许多新的表面处理工艺方法来移除或者控制熔石英玻璃表面缺陷。该研究提出了一种基于反应离子刻蚀(RIE)为基础的新型表面处理工艺以制造高质量的熔石英光学元件,并且拟合了刻蚀深度与缺陷(与激光损伤相关)变化之间的函数关系,用以研究RIE处理对于激光损伤阈值的影响。结果表明,经该工艺得到的样品表面杂质缺陷得到了去除,并有效地预防激光损伤的发生,同时在刻蚀期间表面产生了化学结构相对单一稳定、碳原子浓度较低的高纯度硅表面,刻蚀样品的激光损伤阈值显著提高。该项研究有助于对未来高激光损伤阈值熔石英光学元件的发展。
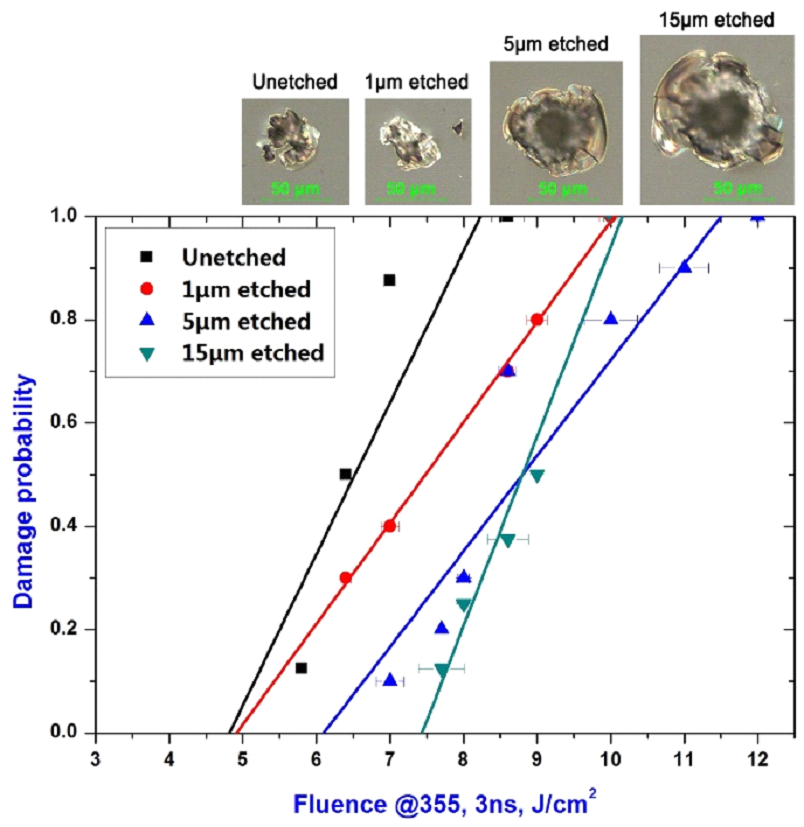
图一 熔石英样品损伤概率和表面形貌
2、使用一种开关照明方案的钢板表面缺陷检测(Steel-surface defect detection using a switching-lighting scheme)【Applied Optics】
DOI: 10.1364/ AO.55.000047
Published:2015/12/22
DOI: 10.1364/ AO.55.000047
Published:2015/12/22
由于钢板表面有着不均匀的亮度和各种形状的缺陷,这导致使用传统的单光源照明方案检测缺陷将十分困难。为了解决这个问题,该文提出了一种新的双光源开关切换照明方案以及相应的滤波算法。图二即单光源照明与双光源开关切换照明(DLSL)结构图,采用DLSL方案,无论大小、形状以及方向缺陷均可以表示为交替的黑白图案,这可以有效减小表面亮度不均匀产生的影响并提高检测精度,如图三所示。此外,钢板图像的纹理由于温度、钢板的等级差别较大而变化明显,因此又提出了一种基于Retinex算法和一般有限脉冲响应滤波的次优算法来补偿DLSL方法得到图像,使仅在缺陷处得到交替的黑白图案,而其余背景处滤掉,如图四所示,这也是该文提出的照明方法和图像处理算法相结合的核心思想。
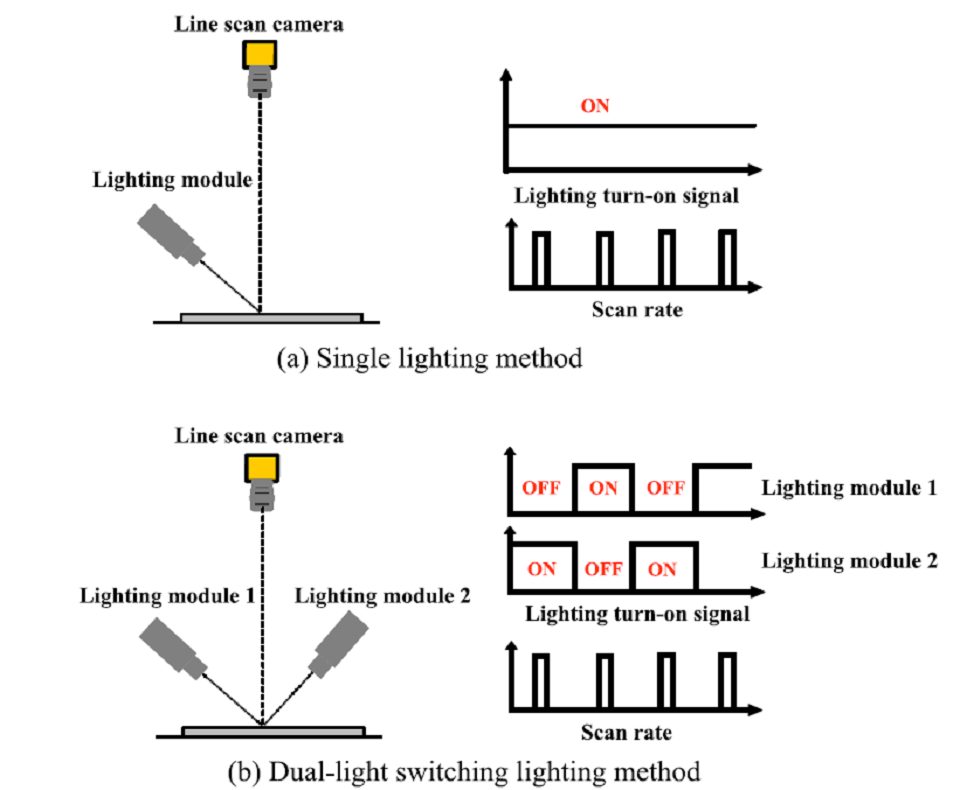
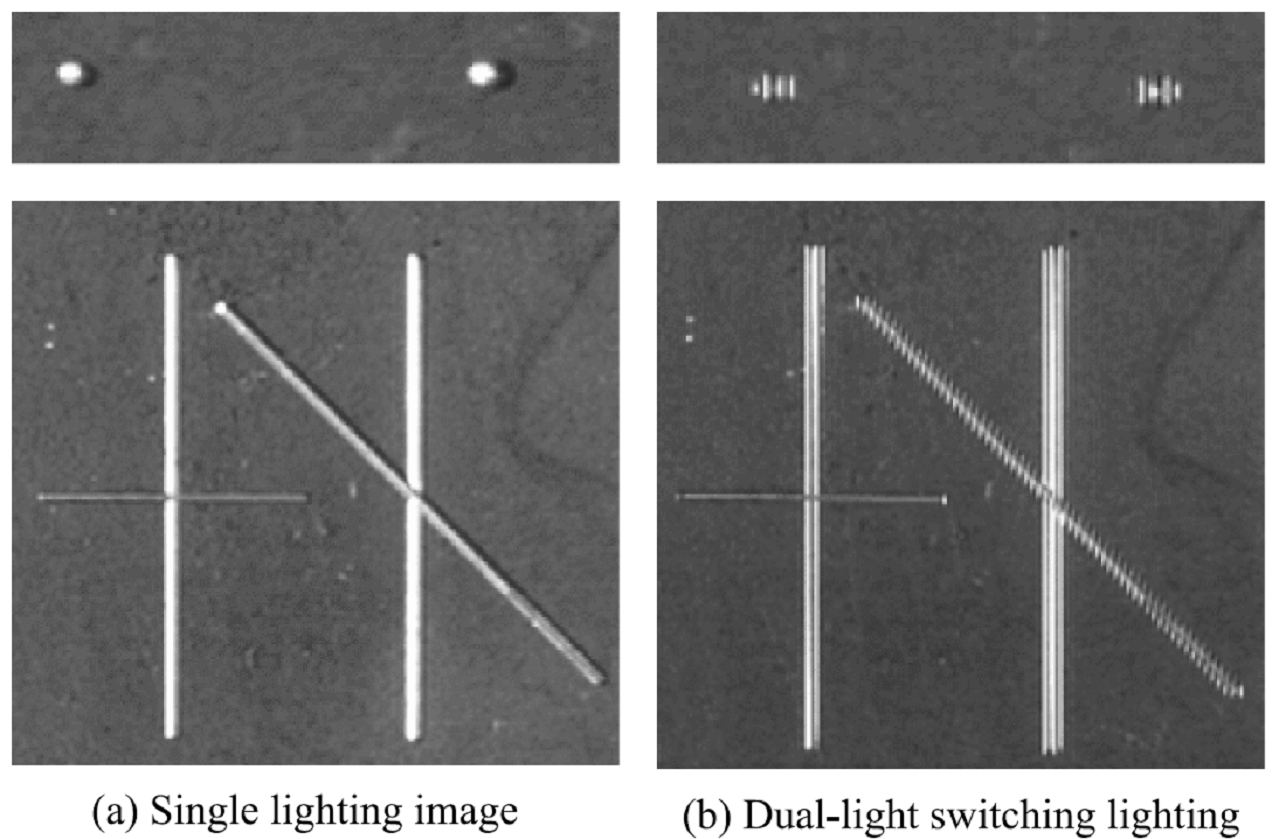
图二 照明结构对比图 图三 不同照明条件下得到的缺陷图像
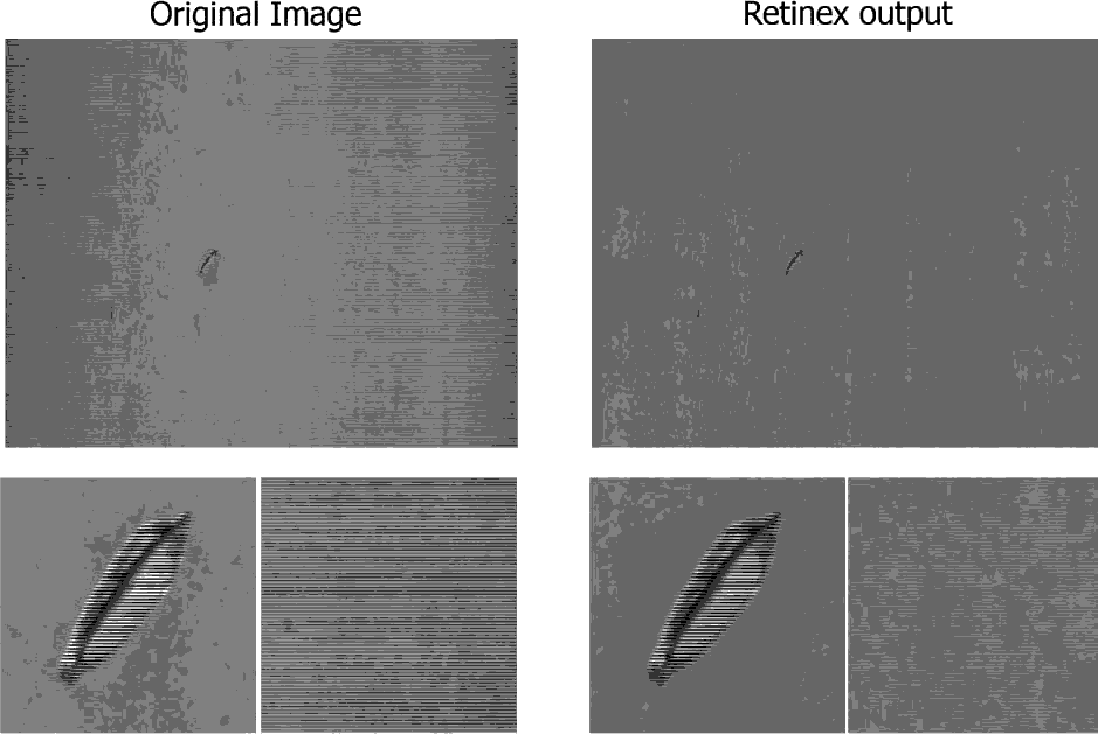
图四 滤波算法后结果

图四 滤波算法后结果
二、简讯:
1、减少气洞内表面缺陷实现少模光子晶体光线损耗降低(Loss reduction in few-mode photonic crystal fiber by reducing inner surface imperfections in air holes)【OPTICS EXPRESS】
DOI: 10.1364/ OE.23.013619
Published:2015/5/15
1、减少气洞内表面缺陷实现少模光子晶体光线损耗降低(Loss reduction in few-mode photonic crystal fiber by reducing inner surface imperfections in air holes)【OPTICS EXPRESS】
DOI: 10.1364/ OE.23.013619
Published:2015/5/15
Abstract:
We studied both theoretically and experimentally the additional loss in photonic crystal fiber (PCF) that results from inner surface imperfections such as contamination and the surface roughness of air holes. We estimated the modal loss dependence of these imperfections using a model with a “defective layer” for the first time. The theoretical studies suggest that higher order modes have a larger loss due to imperfections in the air holes. By minimizing the inner surface imperfections of the six innermost air holes, we can theoretically expect any additional loss to be reduced to a negligible level. Moreover, we examined our theoretical prediction experimentally. We fabricated few-mode PCFs by employing a suitable inner surface treatment for just the six innermost holes. As expected theoretically, the transmission loss was greatly reduced by employing these processes. The lowest transmission losses in the 1550 nm band were 0.31 dB/km for the LP01 mode and 0.43 dB/km for the LP11 mode. Our theoretical model will be useful with a view to realizing few-mode PCF with a loss comparable to that of conventional fibers.
2、利用容差相移算法和连续横向剪切干涉仪测量空间相干函数模量(Measuring the modulus of the spatial coherence function using an error tolerant phase shifting algorithm and a continuous lateral shearing interferometer)【OPTICS EXPRESS】
DOI: 10.1364/ OE. 24.005087
Published:2016/3/1
DOI: 10.1364/ OE. 24.005087
Published:2016/3/1
Abstract:
The modulus of the degree of coherence can be derived from interference patterns either by using fringes and next neighbour operations or by using several interferograms produced through phase shifting. Here the latter approach will be followed by using a lateral shearing interferometer exploiting a diffractive grating wedge providing a linearly progressive shear. Phase shifting methods offer pixel-oriented evaluations but suffer from instabilities and drifts which is the reason for the derivation of an error immune algorithm. This algorithm will use five π/2-steps of the reference phase also for the calculation of the modulus of the coherence function.
3、超分辨离焦全光相机:基于波动光学方法(Super-resolution in a defocused plenoptic camera: a wave-optics-based approach)【Optics Letters】
DOI: 10.1364/ OL.41.000998
Published:2016/2/26
DOI: 10.1364/ OL.41.000998
Published:2016/2/26
Abstract:
Plenoptic cameras enable the capture of a light field with a single device. However, with traditional light field rendering procedures, they can provide only low-resolution two-dimensional images. Super-resolution is considered to overcome this drawback. In this study, we present a superresolution method for the defocused plenoptic camera (Plenoptic 1.0), where the imaging system is modeled using wave optics principles and utilizing low-resolution depth information of the scene. We are particularly interested in super-resolution of in-focus and near in-focus scene regions, which constitute the most challenging cases. The simulation results show that the employed wave-optics model makes super-resolution possible for such regions as long as sufficiently accurate depth information is available.
4、利用多光源的波长扫描干涉法(Wavelength scanning interferometry using multiple light sources)【OPTICS EXPRESS】
DOI: 10.1364/ OE.24.005311
Published:2016/3/2
DOI: 10.1364/ OE.24.005311
Published:2016/3/2
Abstract:
A novel sensing method is proposed for wavelength scanning interferometry using multiple tunable light sources. As it is well known, a deterioration of depth resolution usually occurs when multiple phase intervals, corresponding to the multiple tunable light sources, are used for distance measurement purposes. It is shown here, that it is possible to regain depth resolution characteristics of a complete scan by means of a temporal phase unwrapping extrapolation method. With the proposed method, the resulting phase differences among multiple phase intervals can be successfully unwrapped to find out the intermediate phase. This effectively allows the application of whole-scan phase sensing for distance measurement using reduced scanning intervals, increased speed, and improved depth detection.
供稿:张毅晖







