一、本期重点:
1.Hertbeat OCT:活体血管内兆赫兹OCT(Heartbeat OCT: in vivo intravascular megahertz-optical coherence tomography)【Biomedical Optics Express】
doi: 10.1364/BOE.6.005021
published:2015.11.23
内容介绍:
血管内光学相干断层扫描(IV-OCT)可以提供关于冠状动脉病变和介入治疗的非常详细的图像,在过去的几年中得到了广泛的应用。对比于剖视图,横向截面图像和三维图像受心脏运动和欠采样的影响,使得辨识和测量变得困难。该文介绍了研究组开发的Heartbeat OCT系统,以解决这些问题。
这项研究证明了Heartbeat OCT在成像上消除了心脏运动伪影、以及欠采样和非均匀旋转变形带来的影响。该OCT系统基于兆赫兹扫频光源,用微型马达驱动导管,以100毫米/秒的速度拉回,在一个心动周期内进行密集数据采样。Heartbeat OCT达到体外5600帧/秒和体内4000帧/秒的成像的速度,分别对应18微米和25微米的帧间距。成像结果显示了动脉的光滑内腔,以及清晰可辨的结构,如分支、微血管、皮瓣等在商用IV-OCT中无法准确分辨的结构。
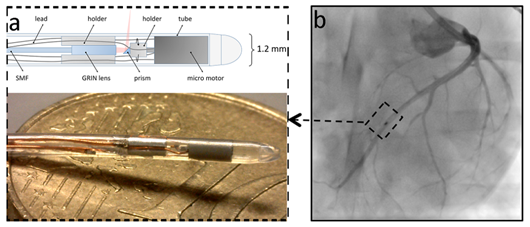
图一:血管内导管的探针针尖,包括光学聚焦系统和微型马达驱动的转镜系统。
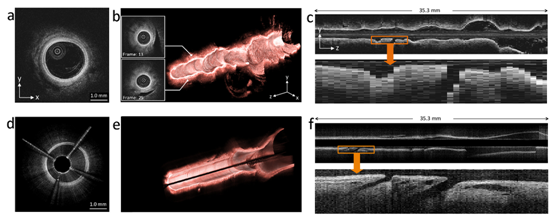
图二:图a、图b和图c是商业OCT的成像,100帧/秒、20毫米/秒;图d、图e和图f是Heartbeat OCT的成像,3200帧/秒、100毫米/秒;分支结构在Heartbeat OCT中可以更清楚地显示出来。
2. 利用相位滤波器扩展焦深的光学探针的设计和制造(Design and fabrication of an optical probe with a phase filter for extended depth of focus)【Optics Express】
doi: 10.1364/OE.24.001037
published:2016.1.12
内容介绍:
聚焦光斑大小和焦深之间的折衷经常限制了光学系统的性能,例如在光学相干断层扫描系统和光镊系统中。尽管研究人员已经提出了各种方法来延长自由空间光学系统的焦深,但由于的空间限制,很多都难以在微型光学探针中实现。这项研究提出了一种光学探针,使用二进制相空间滤波器(BPSF)扩展焦深。所述的BPSF图案,利用复制模塑软光刻技术(replica molding soft lithography),被制作在1毫米直径的光学探针尖端。由于结构简单,它可以很容易地在一个小型化光学探针上实现。通过优化BPSF的设计,可以提升焦深和光效,同时保证光斑直径。通过测量BPSF探针的三维点扩散函数和与没有BPSF的探针进行比较评价,该BPSF探针焦点光斑直径为3.56微米,焦深为199.7微米,而没有BPSF的探针焦点光斑直径为3.69微米,焦深为73.9微米,焦深扩展为2.7倍。该光学探针可以在生物医学中得到应用。
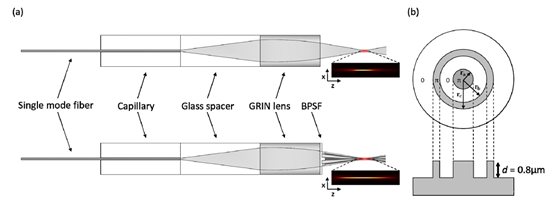
图一:BPSF的结构以及安装了BPSF的探针结构。
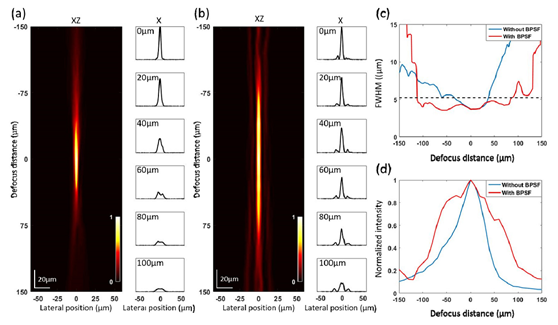
图二:安装BPSF前后的三维点扩散函数测量结果对比。
二、简讯:
1.动脉粥样硬化斑块的多模式光学成像和特征描述(Multi-modal optical imaging characterization of atherosclerotic plaques)【Journal of Biophotonics】
doi: 10.1002/jbio.201500223
published:2015.11.25
Abstract:
We combined cross-polarization optical coherence tomography (CP OCT) and non-linear microscopy based on second harmonic generation (SHG) and two-photon-excited fluorescence (2PEF) to assess collagen and elastin fibers and other vascular structures in the development of atherosclerosis, including identification of vulnerable plaques, which remains an important clinical problem and imaging application. CP OCT's ability to visualize tissue birefringence and cross-scattering adds new information about the microstructure and composition of the plaque. However its interpretation can be ambiguous, because backscattering contrast may have a similar appearance to the birefringence related fringes. Our results represent a step towards minimally invasive characterization and monitoring of different stages of atherosclerosis, including vulnerable plaques.
CP OCT image of intimal thickening in the human coronary artery. The dark stripe in the cross-polarization channel (arrow) is a polarization fringe related to the phase retardation between two eigen polarization states. It is histologically located in the area of the lipid pool, however this stripe is a polarization artifact, rather than direct visualization of the lipid pool.
2. 基于色散的受激拉曼散射光谱、全息和光学相干断层扫描(Dispersion-based stimulated Raman scattering spectroscopy, holography, and optical coherence tomography)【Optics Express】
doi: 10.1364/OE.24.001037
published:2016.1.12
Abstract:
Stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) enables fast, high resolution imaging of chemical constituents important to biological structures and functional processes, both in a label-free manner and using exogenous biomarkers. While this technology has shown remarkable potential, it is currently limited to point scanning and can only probe a few Raman bands at a time (most often, only one). In this work we take a fundamentally different approach to detecting the small nonlinear signals based on dispersion effects that accompany the loss/gain processes in SRS. In this proof of concept, we demonstrate that the dispersive measurements are more robust to noise compared to amplitude-based measurements, which then permit spectral or spatial multiplexing (potentially both, simultaneously). Finally, we illustrate how this method may enable different strategies for biochemical imaging using phase microscopy and optical coherence tomography.
3.食管壁的活体OCT栓线胶囊内镜显微图像的自动分割和特征描述(Automated segmentation and characterization of esophageal wall in vivo by tethered capsule optical coherence tomography endomicroscopy)【Biomedical Optics Express】
doi: 10.1364/BOE.7.000409
published:2016.1.8
Abstract:
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an optical diagnostic modality that can acquire cross-sectional images of the microscopic structure of the esophagus, including Barrett’s esophagus (BE) and associated dysplasia. We developed a swallowable tethered capsule OCT endomicroscopy (TCE) device that acquires high-resolution images of entire gastrointestinal (GI) tract luminal organs. This device has a potential to become a screening method that identifies patients with an abnormal esophagus that should be further referred for upper endoscopy. Currently, the characterization of the OCT-TCE esophageal wall data set is performed manually, which is time-consuming and inefficient. Additionally, since the capsule optics optimally focus light approximately 500 µm outside the capsule wall and the best quality images are obtained when the tissue is in full contact with the capsule, it is crucial to provide feedback for the operator about tissue contact during the imaging procedure. In this study, we developed a fully automated algorithm for the segmentation of in vivo OCT-TCE data sets and characterization of the esophageal wall. The algorithm provides a two-dimensional representation of both the contact map from the data collected in human clinical studies as well as a tissue map depicting areas of BE with or without dysplasia. Results suggest that these techniques can potentially improve the current TCE data acquisition procedure and provide an efficient characterization of the diseased esophageal wall.
4.活体光声成像用于肌红蛋白氧饱和度测量(In vivo photoacoustic tomography of myoglobin oxygen saturation)【Journal of Biomedical Optics】
doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.21.6.061002
published:2015.12.17
Abstract:
Myoglobin is an essential oxygen-binding hemoprotein in skeletal and cardiac muscles that buffers intracellular oxygen (O2) concentration in response to hypoxia or elevated muscle activities. We present a method that uses photoacoustic computed tomography to measure the distribution of myoglobin in tissue and the oxygen saturation of myoglobin (sO2-Mb). From photoacoustic measurements of mice in different oxygenation states, we performed calibration-free quantification of the sO2-Mb change in the backbone muscle in vivo.
供稿:陈志彦







