一、本期重点:
doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298634
date of conference: 2015.6.7-12
内容简介:
在各类图像复原算法中,模糊核估计一直是一项重要的工作,根据图像降质的情况不同,模糊核估计的难度也有很大的变动。文章利用各种方法获取得到多个图像模糊核,通过基于数据驱动的核融合手段构建出一个更加精准的图像PSF,使之应用于图像复原中,最终获得更好的图像质量。文章中也对各类模糊核融合模型进行了深入讨论,通过比较发现基于高斯条件随机场的融合方法效果最好。
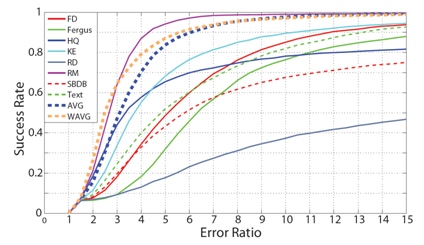
图1. 各类融合方法效果比较
doi:10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298665
date of conference: 2015.6.7-12
内容简介:
最小可察觉离焦模糊(JNB)是由于图像拍摄时目标场景未准确对焦从而引起图像存在几个像素的模糊量扩散的一类问题。由于离焦图像带有一定的深度信息,理论上可以通过提取获得深度信息,以此作为图像去模糊的基础工作,但实际上目前基于局部信息的离焦模糊方法并不能识别该类较小离焦量的模糊图像。文章提出了基于稀疏表征和图像分解的模糊特征描述方法,直接将稀疏边缘表征和模糊量估计联系起来。图像复原的效果证明了该类方法的高效性。
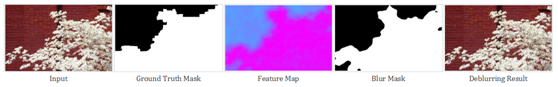
图1. 模糊估计的方法流程

图2. 不同深度离焦量的模糊图像信息提取
二、简讯:
doi:10.1109/ICCPHOT.2014.6831807
date of conference: 2014.5.2-4
Abstract:
Building high dynamic range (HDR) images by combining photographs captured with different exposure times present several drawbacks, such as the need for global alignment and motion estimation in order to avoid ghosting artifacts. The concept of spatially varying pixel exposures (SVE) proposed by Nayar et al. enables to capture in only one shot a very large range of exposures while avoiding these limitations. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to generate HDR images from a single shot acquired with spatially varying pixel exposures. The proposed method makes use of the assumption stating that the distribution of patches in an image is well represented by a Gaussian Mixture Model. Drawing on a precise modeling of the camera acquisition noise, we extend the piecewise linear estimation strategy developed by Yu et al. for image restoration. The proposed method permits to reconstruct an irradiance image by simultaneously estimating saturated and under-exposed pixels and denoising existing ones, showing significant improvements over existing approaches.
doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2015.2411575
published:2015.3.9
Abstract:
A blind compressive sensing algorithm is proposed to reconstruct hyperspectral images from spectrally-compressed measurements. The wavelength-dependent data are coded and then superposed, mapping the three-dimensional hyperspectral datacube to a two-dimensional image. The inversion algorithm learns a dictionary in situ from the measurements via global-local shrinkage priors. By using RGB images as side information of the compressive sensing system, the proposed approach is extended to learn a coupled dictionary from the joint dataset of the compressed measurements and the corresponding RGB images, to improve reconstruction quality. A prototype camera is built using a liquid-crystal-on-silicon modulator. Experimental reconstructions of hyperspectral datacubes from both simulated and real compressed measurements demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed inversion algorithm, the feasibility of the camera and the benefit of side information.
doi: 10.1364/OL.40.004054
published:2015.8.26
Abstract:
This Letter presents a compressive camera that integrates mechanical translation and spectral dispersion to compress a multi-spectral, high-speed scene onto a monochrome, video-rate detector. Experimental reconstructions of 17 spectral channels and 11 temporal channels from a single measurement are reported for a megapixel-scale monochrome camera.
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2335751
published:2014.7.25
Abstract:
Ship detection on spaceborne images has attracted great interest in the applications of maritime security and traffic control. Optical images stand out from other remote sensing images in object detection due to their higher resolution and more visualized contents. However, most of the popular techniques for ship detection from optical spaceborne images have two shortcomings: 1) Compared with infrared and synthetic aperture radar images, their results are affected by weather conditions, like clouds and ocean waves, and 2) the higher resolution results in larger data volume, which makes processing more difficult. Most of the previous works mainly focus on solving the first problem by improving segmentation or classification with complicated algorithms. These methods face difficulty in efficiently balancing performance and complexity. In this paper, we propose a ship detection approach to solving the aforementioned two issues using wavelet coefficients extracted from JPEG2000 compressed domain combined with deep neural network (DNN) and extreme learning machine (ELM). Compressed domain is adopted for fast ship candidate extraction, DNN is exploited for high-level feature representation and classification, and ELM is used for efficient feature pooling and decision making. Extensive experiments demonstrate that, in comparison with the existing relevant state-of-the-art approaches, the proposed method requires less detection time and achieves higher detection accuracy.
供稿:黄加紫







