一、 本期重点:
1.光学相干光声显微镜实现在体多模式的视网膜成像(Optical coherence photoacoustic microscopy for in vivo multimodal retinal imaging)【OPTICS LETTERS】
DOI:10.1364/OL.40.001370
Published:2015.3.23
内容介绍:
光学相干层析成像从低相干反射仪发展而来,通过检测生物组织对入射的弱相干光的背向散射信号成像。能够对微小的生物组织结构进行成像,在视网膜成像方面已经被广泛运用。光声显微镜也是一个三维无损的成像方法,通过利用生物组织的光学吸收特性成像。在微血管结构和生物组织中血氧的研究方面运用较多。本文介绍了光学相干光声显微镜系统,通过利用一个单脉冲宽带光源,能够实现光学相干层析成像和光声显微镜的同时成像。该系统能同时捕捉来自样品的光学散射信息和光学吸收特性,从而更全面的展示样品的特征。系统光源的中心波长是800纳米,带宽为30纳米,适合于视网膜成像。但血红蛋白对该波长的吸收相对较弱,所以近红外光声成像主要针对于眼后段的黑色素,所以也提供了一种表明视网膜黑色素特性的成像方法。
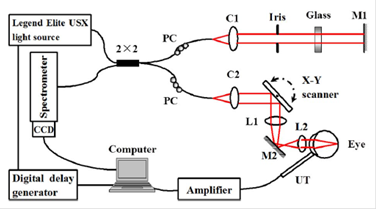
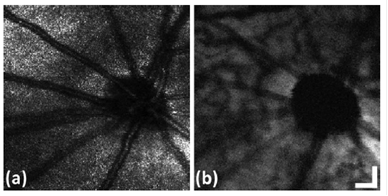
图2:同时得到的兔子视网膜的光学相干层析成像图(a)和光声图(b)
2.基于高速无标签功能性光声显微镜的运转中的鼠脑成像 (High-speed label-free functional photoacoustic microscopy of mouse brain in action)【Nature Methods】
DOI:10.1038/nmeth.3336
Published:2015.3.30
内容介绍:
文章报道了一种快速功能性光声显微镜,能在完好的保留头盖骨的情况下在体实现高分辨率、高速鼠脑成像。在针对血氧的成像中系统能实现一维方向上的成像速度为100kHz,并拥有毛细血管水平的分辨率。通过该系统,成功实现对放松状态以及刺激状态下的血管形态、血氧、血流以及氧代谢等的成像。
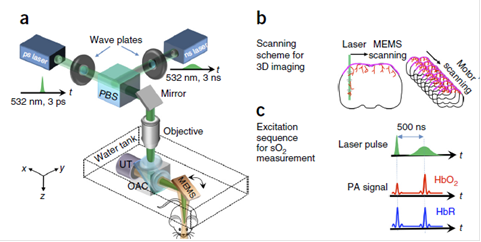

图3:针对鼠脑成像的快速功能性光声显微镜。(a) 系统原理图 (b) 系统扫描方案。系统的三维成像,通过在X轴方向上的快速微机电镜扫描以及y方向上较慢的电机扫描实现 (c) 光声的激发和探测序列。由于不同的氧饱和度,皮秒脉冲打到氧和血红蛋白上时得到的光声的振幅信息会略小于下一个脉冲;而当皮秒脉冲打到脱氧血红蛋白上时,影响就会微不足道 (d) 典型的xy方向投影的通过完整头盖骨得到的脑部血管成像 (e) 典型的加强型xz方向投影的脑血管成像 (f) 在同一只鼠脑中得到的血红蛋白氧饱和光声图
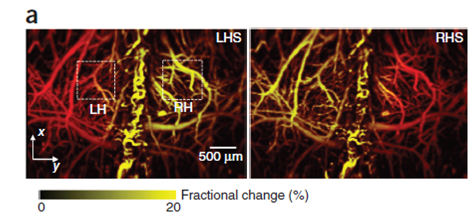
图4:通过对老鼠下肢电刺激得到的大脑反应光声图。左下肢刺激(LHS)和右下肢刺激 (RHS)图。
二、简讯:
DOI:10.1364/BOE.6.000369
We demonstrate a prototype system of polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography (PS-OCT) designed for clinical studies of the anterior eye segment imaging. The system can measure Jones matrices of the sample with depth-multiplexing of two orthogonal incident polarizations and polarization-sensitive detection. An optical clock is generated using a quadrature modulator and a logical circuit to double the clock frequency. Systematic artifacts in measured Jones matrices are theoretically analyzed and numerically compensated using signals at the surface of the sample. Local retardation images of filtering blebs after trabeculectomy show improved visualization of subconjunctival tissue, sclera, and scar tissue of the bleb wall in the anterior eye segment.
DOI: 10.1038/NPHOTON.2014.322
Published:2015.1.19
Non-invasively focusing light into strongly scattering media, such as biological tissue, is highly desirable but challenging. Recently, ultrasonically guided wavefront-shaping technologies have been developed to address this limitation. So far, the focusing resolution of most implementations has been limited by acoustic diffraction. Here, we introduce nonlinear photoacoustically guided wavefront shaping (PAWS), which achieves optical diffraction-limited focusing in scattering media. We develop an efficient dual-pulse excitation approach to generate strong nonlinear photoacoustic signals based on the Grueneisen relaxation effect. These nonlinear photoacoustic signals are used as feedback to guide iterative wavefront optimization. As a result, light is effectively focused to a single optical speckle grain on the scale of 5–7 μm, which is ∼10 times smaller than the acoustic focus, with an enhancement factor of ∼6,000 in peak fluence. This technology has the potential to benefit many applications that require a highly confined strong optical focus in tissue.
3.小散射样本中的在体光学断层成像:头部外翻的黑腹果蝇的延时三维成像(In-vivo Optical Tomography of Small Scattering Specimens: time-lapse 3D imaging of the head eversion process in Drosophila melanogaster)
DOI: 10.1038/srep07325
Published:2014.12.4
Even though in vivo imaging approaches have witnessed several new and important developments, specimens that exhibit high light scattering properties such as Drosophila melanogaster pupae are still not easily accessible with current optical imaging techniques, obtaining images only from subsurface features. This means that in order to obtain 3D volumetric information these specimens need to be studied either after fixation and a chemical clearing process, through an imaging window - thus perturbing physiological development -, or during early stages of development when the scattering contribution is negligible. In this paper we showcase how Optical Projection Tomography may be used to obtain volumetric images of the head eversion process in vivo in Drosophila melanogaster pupae, both in control and headless mutant specimens. Additionally, we demonstrate the use of Helical Optical Projection Tomography (hOPT) as a tool for high throughput 4D-imaging of several specimens simultaneously.
4.基于前房角OCT系统实现虹膜角膜角的360度圆周成像(Complete 360° circumferential gonioscopic optical coherence tomography imaging of the iridocorneal angle)
DOI:10.1364/BOE.6.001376
Published:2015.3.20
Abstract:
Clinically, gonioscopy is used to provide en face views of the ocular angle. The angle has been imaged with optical coherence tomography (OCT) through the corneoscleral limbus but is currently unable to image the angle from within the ocular anterior chamber. We developed a novel gonioscopic OCT system that images the angle circumferentially from inside the eye through a custom, radially symmetric, gonioscopic contact lens. We present, to our knowledge, the first 360° circumferential volumes (two normal subjects, two subjects with pathology) of peripheral iris and iridocorneal angle structures obtained via an internal approach not typically available in the clinic.
供稿:倪秧







