一、本期重点:
1.基于光学微光纤三光束干涉仪的折射率传感器(Demonstration of a refractometric sensor based on an optical micro-fiber three-beam interferometer)【Scientific Reports】
doi: 10.1038/srep07504
published:2014.12.16
内容介绍:
随着光纤的直径接近导光波长并且芯与包层的折射率差变大,光学微光纤表现出多种有趣的波导特性,包括大范围可调的光束缚、强倏逝场和波导色散等。在微光纤众多的应用中,由于可能实现光纤光学传感器的高灵敏度、低能耗及小型化,光学传感受的研究到越来越多的关注。目前已提出典型的基于微光纤传感的结构有迈克尔逊干涉仪、马赫-曾德干涉仪、法布里-伯罗干涉仪、微光纤环形谐振器等。这些结构的灵敏度极大程度依赖于微光纤外部的倏逝场。文章报道了一种基于微光纤三光束干涉仪的新型折射率传感器的首次理论和实验研究成果。理论和实验分析表明传感器的灵敏度不仅由微光纤外的倏逝场决定,同时也与干涉臂的值有关。当干涉臂的有效长度接近相等时,检测灵敏度会得到很大提高,这一点在提升折射率探测的灵敏度方面具有很大潜能。
图1为三光束干涉仪(TBI)结构示意图。这个干涉仪系统包括一个马赫-曾德干涉系统和一个Sagnac环。当入射光由图1(b)输入端进入后被第一个耦合器分为两束,两束光分别传播后经第二个耦合器进入Sagnac环路后再次回到第一个耦合器中,TBI在输出端的总光场是三个具有不同相位延迟的光场的和。图2为臂长和折射率不同时,两种参数TBI的输出光谱。
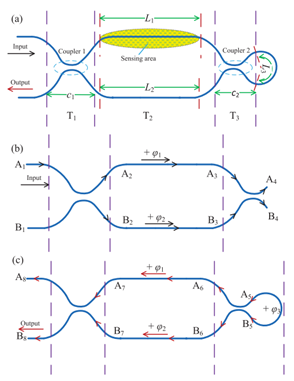
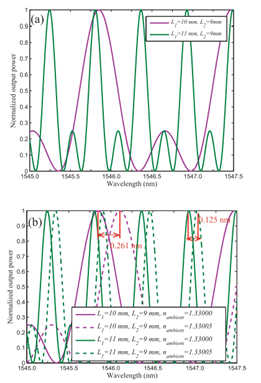
图1 图2
(a)微光纤三光束干涉仪结构 (a)臂长不同的两种TBI的输出光谱
(b)和(c)分别为光的入射和出射光路 (b)周围折射率不同时的输出光谱
doi:10.1364/OL.39.006855
published:2014.12.10
内容介绍:
文章为据作者所知的第一篇关于三维全景成像捕获和传感器位置未知的灵活表面重构方法的报道。传统的全景成像系统通常采用微透镜或传感器阵列固定在一个平面表面,而文中提出的曲面感知全景成像系统可使传感器放置在非平面的表面,因此扩大了3D成像系统的视场。为了得到弯曲表面上传感器阵列的位姿,提出了基于双观测几何理论的估计算法和相机投影模型。此外,还从一系列低分辨率的2D图像中采用亚像素位移得到了超分辨率图像,给出不同深度的超分辨率3D重构结果证实了所提方法的有效性。
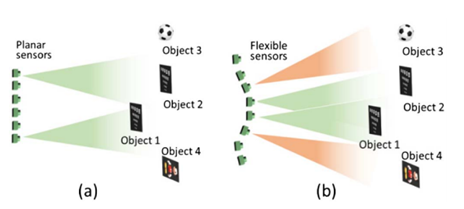
图4为传统全景成像系统和曲面感知全景成像系统的最左和最右视场,图5给出了采用超分辨算法与未采用超分辨算法的重构结果对比图。
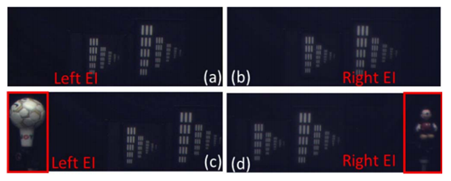
图4曲面感知的视场扩大 (a)(b)分别为传统系统的最左、最右成像图 (c)(d)分别为曲面感知系统最左、最右成像图
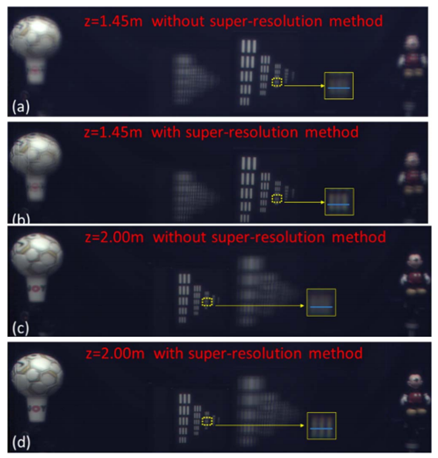

图5不采用和采用超分辨重构技术的曲面感知全景成像结果对比 (a)(b)分别为在距离1.45m处聚焦于右侧分辨率板时不采用和采用超分辨重构技术的计算机重构结果(c)(d)分别为距离2.00m处聚焦于左侧分辨率板时不采用和采用该技术的结果。
二、简讯:
doi:10.1364/OL.39.006954
published:2014.12.12
Abstract:
We demonstrate a scanning fiber-optic probe for magnetic-field imaging where nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers are coupled to an optical fiber integrated with a two-wire microwave transmission line. The electron spin of NV centers in a diamond microcrystal attached to the tip of the fiber probe is manipulated by a frequency-modulated microwave field and is initialized by laser radiation transmitted through the optical tract of the fiber probe. The two-dimensional profile of the magnetic field is imaged with a high speed and high sensitivity using the photoluminescence spin-readout return from NV centers, captured and delivered by the same optical fiber.
doi:10.1364/OE.22.032220
published:2014.12.22
Abstract:
The accuracy performance of fringe projection profilometry (FPP) depends on accurate phase-to-height (PTH) mapping and system calibration. The existing PTH mapping is derived based on the condition that the plane formed by axes of camera and projector is perpendicular to the reference plane, and measurement error occurs when the condition is not met. In this paper, a new geometric model for FPP is presented to lift the condition, resulting in a new PTH mapping relationship. The new model involves seven parameters, and a new system calibration method is proposed to determine their values. Experiments are conducted to verify the performance of the proposed technique, showing a noticeable improvement in the accuracy of 3D shape measurement.
doi:10.1364/AO.53.008463
published:2014.12.17
Abstract:
This paper deals with interference fringe center detection techniques used in low-coherence interferometry for contactless 3D inspection of macroscopic objects. It presents a complex analysis of several frequently used detection techniques and shows their impact on the measurement accuracy. The analysis compares those techniques in terms of computational complexity, measurement accuracy, and resistance to optical dispersion caused by wedge-shaped optical components.
doi:10.1364/AO.53.008268
published:2014.12.04
Abstract:
In a previous contribution [Appl. Opt. 51, 8599 (2012)], a coauthor of this work presented a method for reconstructing the wavefront aberration from tangential refractive power data measured using dynamic skiascopy. Here we propose a new regularized least squares method where the wavefront is reconstructed not only using tangential but also sagittal curvature data. We prove that our new method provides improved quality reconstruction for typical and also for highly aberrated wavefronts, under a wide range of experimental error levels. Our method may be applied to any type of wavefront sensor (not only dynamic skiascopy) able to measure either just tangential or tangential plus sagittal curvature data.
供稿:师途







