一、本期重点:
1.通过空间烧孔相互作用的控制来增强激光功效(Enhancement of laser power-efficiency by control of spatial hole burning interactions)【Nature Photonics】
doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.244
published:2014.10.26
内容介绍:
激光是非平衡的非线性系统,在增益介质参与下的谐振腔的结构和非线性波之间的相互作用,决定了激光的自振荡频率和相关的空间场图案。激光处于稳态时,有泵浦出的稳定光子流出射,输出能量与输入能量的比值称为能量效率。虽然非线性波的相互作用在激光理论的早期即被建模和理解,但它们对激光系统能量效率的影响没有被很好地解释。空间烧孔效应通常降低了能量效率,文中阐述了空间烧孔效应能被一个空间拖尾的泵浦截面所控制,从而使激光的能量效率提高几个数量级。
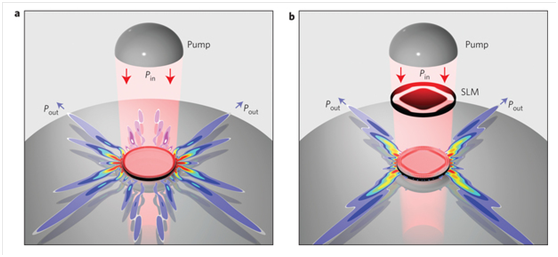
图一 (a)常规泵浦下的高品质因子的回音壁谐振腔(b)结构中加入了空间光调制器将空间光模式选取为特定形态
doi:10.1364/OL.39.006466
published:2014.11.11
内容介绍:
文中提出了一种大型复杂光场的成像方法,通过使用编码孔径的单次相位成像的方法,不仅可以获得物体的振幅信息,也可以获得物体的相位信息。物体被相干的可见光照射后被编码孔径编码,编码后的光场被图像接收器接收。被编码后的光场通过相位恢复算法可被提取出相关信息,这是通过相关的稀疏条件限制和压缩感知的方法。文中提出了理论模型,同时进行了数据验证。
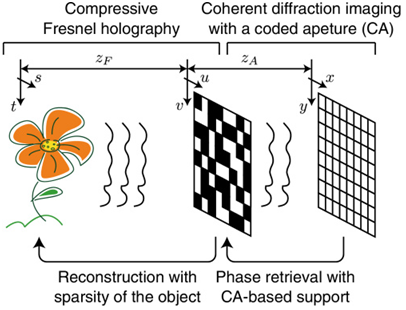
图二 系统原理图
二、简讯:
doi:10.1364/OE.22.030257
published:2014.11.26
Abstract:
In this article we present a new all-optical method to measure elastic constants connected with twist and bend deformations. The method is based on the optical Freedericksz threshold effect induced by the linearly polarized electro-magnetic wave. In the experiment elastic constants are measured of commonly used liquid crystals 6CHBT and E7 and two new nematic mixtures with low birefringence. The proposed method is neither very sensitive on the variation of cell thickness, beam waist or the power of a light beam nor does it need any special design of a liquid crystal cell. The experimental results are in good agreement with the values obtain by other methods based on an electro-optical effect.
doi:10.1364/OE.22.029515
published:2014.11.18
Abstract:
High-end lenses are usually composed of many optical elements to compensate various optical aberrations, e.g. geometric distortion, monochromatic and chromatic aberrations. The resulting complexity and machining accuracy requirements make high-end lenses too expensive, heavy, and fragile for day-to-day photography. To address this problem, we devised an optical computing approach to touch-up the low quality photos produced by simpler lenses. We propose a setup consisting of an easily accessible display and the original camera in order to perform optical aberration correction with a deconvolution framework. The equivalence of the degeneration model and the lens’s optical computing turns the traditional blind deconvolution algorithm into its non-blind counterpart and promises robust performance. A prototype system is implemented to verify the feasibility of the proposed method, and a series of experiments on both synthetic and captured images are applied to demonstrate effectiveness and performance.
doi: 10.1364/OE.22.029340
published:2014.11.17
Abstract:
We show that a classical imaging criterion based on angular dependence of small-angle phase can be applied to any system composed of planar, uniform media to determine if it is a flat lens capable of forming a real paraxial image and to estimate the image location. The real paraxial image location obtained by this method shows agreement with past demonstrations of far-field flat-lens imaging and can even predict the location of super-resolved images in the near-field. The generality of this criterion leads to several new predictions: flat lenses for transverse-electric polarization using dielectric layers, a broadband flat lens working across the ultraviolet-visible spectrum, and a flat lens configuration with an image plane located up to several wavelengths from the exit surface. These predictions are supported by full-wave simulations. Our work shows that small-angle phase can be used as a generic metric to categorize and design flat lenses.
doi: 10.1364/OE.22.029805
published:2014.11.20
Abstract:
We introduce and demonstrate a new high performance image reconstruction method for super-resolution structured illumination microscopy based on maximum a posteriori probability estimation (MAP-SIM). Imaging performance is demonstrated on a variety of fluorescent samples of different thickness, labeling density and noise levels. The method provides good suppression of out of focus light, improves spatial resolution, and allows reconstruction of both 2D and 3D images of cells even in the case of weak signals. The method can be used to process both optical sectioning and super-resolution structured illumination microscopy data to create high quality super-resolution images.
供稿:王恒







