
北京时间10月8日下午,2014年诺贝尔化学奖揭晓,美国及德国三位科学家Eric Betzig、Stefan W. Hell和William E. Moerner获奖。获奖理由是“研制出超分辨率荧光显微镜”。三人将均分800万瑞典克朗奖金。
对于学习光电的我们来说,衍射极限并不陌生:由于衍射的限制,理想物点经过光学系统不可能得到理想像点,而是得到一个夫朗和费衍射像,即艾里斑(Airy Disk)。如果两个物点靠得很近,两个衍射像就叠加在一起,我们看到的就是一团模糊的图像。因此,显微镜学者恩斯特·阿贝(Ernst Abbe) 在1873年给传统的光学显微镜分辨率定下了一个物理极限:它不可能突破0.2微米。现今,今年诺贝尔化学奖的几位获得者巧妙的绕开了这种极限,他们突破性的研究将光学显微带入了纳米维度。
这次获奖的是两项独立的技术。第一项是Stefan Hell于2000年研制的受激发射减损(STED)显微技术。此项技术采用了两束激光;一束负责激发荧光分子使其发光,另一束则负责抵消大部分荧光,只留下一块纳米大小体积的荧光区域。用该技术仔细扫描样本,得出的图像分辨率打破了Abbe提出的显微分辨率极限。
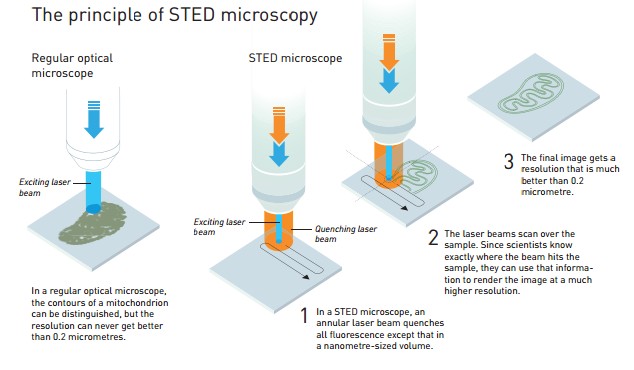
图1 STED的基本原理
Eric Betzig和William Moerner分别独立地进行研究,为第二种技术打下了基础,即单分子显微技术。这种方法依赖于开关单个分子荧光的可能性。科学家对同一区域进行了多次“绘图”,每次仅仅让很少量的分散分子发光。将这些图像叠加起来产生了密集的纳米尺寸超分辨率图像。2006年,Eric Betzig首次采用了这一技术。
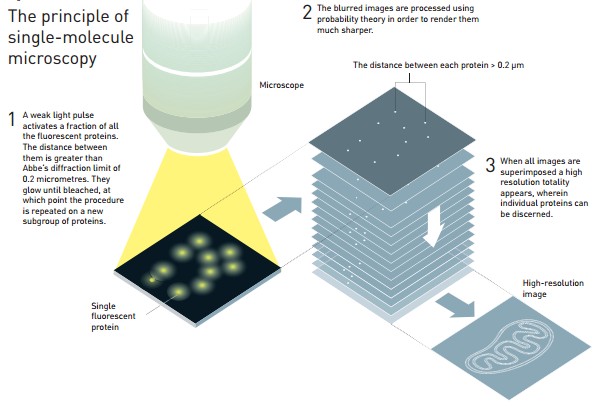
图2 单分子显微成像技术
超分辨技术的研究其实离我们并不遥远,而且也早已在我系开始。显示所刘旭教授、匡翠方副教授、斯科教授等课题组成员从2010年起开始从事超分辨成像技术的相关研究,在研究的两个主要分支上均取得了积极进展。在荧光显微成像领域,搭建了国内首套门控荧光受激发射损耗(g-STED)光学显微系统,并在国内首次实现38 nm (~λ/14)的空间分辨率,并提出了受激发射微分的超分辨方法;在非荧光成像方面,首次提出移频机理的超分辨方法,并在实验上实现了~λ/7分辨率。课题组刘旭教授担任首席科学家的973项目“纳米分辨快速光学成像机理与技术的基础研究”、国家重大科研仪器项目“并行纳米光场调控荧光辐射微分三维超分辨成像系统”和其他基金项目,也将继续围绕“纳米分辨”这一主题开展,为超分辨技术的发展做出自己的贡献!
超分辨技术已经在全球被广泛使用,并且将不断为人类做出新的贡献。
附:与显微术(Microscopy)相关的历届诺贝尔奖项
Richard Zsigmondy developed the ultramicroscope - awarded the 1925 Chemistry Prize.
Frits Zernike invented the phase-contrast microscope - awarded the 1953 Physics Prize.
Ernst Ruska developed the electron microscope – awarded the 1986 Physics Prize.
Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer invented the scanning tunneling microscope - awarded the 1986 Physics Prize .
Aaron Klug developed the crystal ographic electron microscopy - awarded the 1986 Chemistry Prize.
Frits Zernike invented the phase-contrast microscope - awarded the 1953 Physics Prize.
Ernst Ruska developed the electron microscope – awarded the 1986 Physics Prize.
Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer invented the scanning tunneling microscope - awarded the 1986 Physics Prize .
Aaron Klug developed the crystal ographic electron microscopy - awarded the 1986 Chemistry Prize.
显示所超分辨组供稿
2014年10月9日
Richard Zsigmondy developed the ultramicroscope - awarded the 1925 Chemistry Prize.
Frits Zernike invented the phase-contrast microscope - awarded the 1953 Physics Prize.
Ernst Ruska developed the electron microscope – awarded the 1986 Physics Prize.
Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer invented the scanning tunneling microscope - awarded the 1986 Physics Prize .
Aaron Klug developed the crystal ographic electron microscopy - awarded the 1986 Chemistry Prize.
Frits Zernike invented the phase-contrast microscope - awarded the 1953 Physics Prize.
Ernst Ruska developed the electron microscope – awarded the 1986 Physics Prize.
Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer invented the scanning tunneling microscope - awarded the 1986 Physics Prize .
Aaron Klug developed the crystal ographic electron microscopy - awarded the 1986 Chemistry Prize.
显示所超分辨组供稿
2014年10月9日







