一、 本期重点:
doi:10.1364/AO.52.008501
published: 2013.12.04
内容介绍:
失调误差校正一直是非球面非零位检测的一个难题,其中区分高阶失调误差尤其不易。传统方法通过从检测所得波前结果中直接去除前四项泽尼克系数进行校正,这是不准确的。计算机辅助装调是一种有效的装调方法,但是需要借助机械或人力辅助完成,实用性受到影响。文章提出了一种基于系统建模的实用且精确的失调误差校正方法。从实验测得波前的五个低阶像差中计算得到实际失调误差,并将此误差建入系统模型,通过光线追迹可以得到其他所有的失调像差,这些像差通过一个简单的波前相减就可以得到去除。这一方法既不需要精确的机械调整,也不需要繁琐的人为调整。实验结果表明了所提方法的可行性和良好的重复性。
检测波前的五个低阶像差包括x和y方向倾斜、离焦以及x和y方向的慧差,被提取出来用于计算非球面的失调误差。关键在于,这种方法不需要对实际检测系统进行再次调整,而仅依赖于系统建模,适用于装调经验不足的人员在实际生产检测条件下应用。
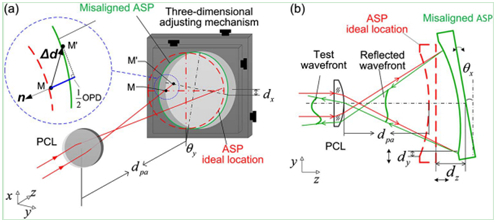
图1 非球面失调示意图。(a)三维图;(b)y-z平面示意图。
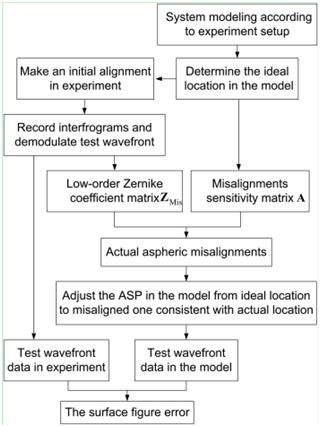
图2 非球面失调误差校正步骤
doi:10.1364/OL.38.005299
published:2013.12.05
内容介绍:
文章介绍了一种新颖的干涉特性描述方案,这种方法可以完全重构出两个相互干涉的光的光场。如果对其中一束光进行剪切,那么两束光的相位分布轮廓及其相对相位就可以同时得到重建。这种方法可以应用于波前传感或超短脉冲测量,尤其还可以用于难以产生参考场或难以复制光束进行自我参照测量的一些极端光源的情况。文章通过实验同时测量了由单个激光器发射的两个超短脉冲,证实了方法可行性。
两独立光场的相互干涉技术可以用于一些利用传统干涉难以进行测量的问题,如测量具有大的互补性频率间隔的脉冲;而且与光谱相位干涉相比,这种方法不需要对线性相位项进行校正。文中所述算法速度很快,足够满足对任意脉冲对进行在线诊断。该方法将对光束的剪切限制转移到更易于控制的第二束参与干涉的独立光,从而保证对第一束检测光的非接触。
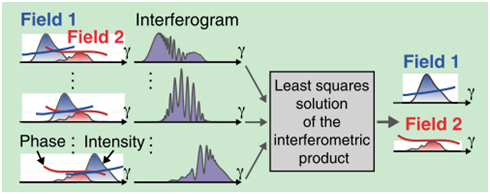
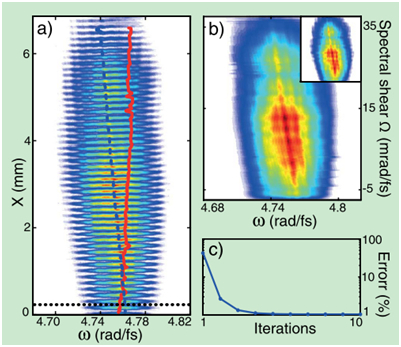
图4 (a)两未知脉冲的干涉图样;蓝色虚线和红色实线为脉冲的光谱剪切轴,黑色点线表示用光谱相位干涉直接重构光场时的剪切情况(b)小插图为原始脉冲波前,大图为经过10此迭代后重建所得脉冲波前(c)重构波前误差
二、 简讯:
doi:10.1364/OL.39.000170
published:2013.12.24
Abstract:
We report on an 800 nm center-wavelength metal/multilayer-dielectric grating (MMDG) with broadband, high diffraction efficiency. The trapezoidal grating ridge consists of an HfO2 layer sandwiched between two SiO2films. Combining the advantages of SiO2andHfO2, the grating ridge reduces the difficulties of grating ridge attainment. For such a configuration, high-performance MMDG can be successfully fabricated using the existing technology. Experimentally we demonstrated a 163 nm bandwidth MMDG with -1st-order diffraction efficiency greater than 90%. The fabricated MMDG achieved high performance as the design with large fabrication tolerances.
doi:10.1364/AO.53.000141
published:2013.12.24
Abstract:
This paper describes a method to determine the phase retardation of birefringent optical components by combining spectral interferometry and the Fourier transform method. The retardation of each orthogonal polarization component was resolved by using two rotatable linear polarizers in the interferometer. The phase retardation measured by using suggested method was compared to that measured using the conventional polarimetric method. The results of independent methods were well matched, which confirms the validity of the proposed method.
doi:10.1364/OE.21.032690
published:2013.12.24
Abstract:
Actively-controlled second harmonic generation in a silicon nitride ring resonator is proposed and simulated. The ring was designed to resonate at both pump and second harmonic wavelengths and quasi-phase-matched frequency conversion is induced by a periodic static electric field generated by voltage applied to electrodes arranged along the ring. Nonlinear propagation simulations were undertaken and an efficiency of −21.67 dB was calculated for 60 mW of pump power at 1550 nm and for a 30V applied voltage, which compares favorably with demonstrated all-optical second harmonic generation in integrated microresonators. Transient effects were also evaluated. The proposed design can be exploited for the construction of electro-optical devices based on nonlinear effects in CMOS compatible circuits..
doi:10.1364/AO.52.007838
published:2013.11.08
Abstract:
Thanks to wavelength flexibility, interferometric filters such as Fabry–Perot interferometers (FPIs) andfield-widened Michelson interferometers (FWMIs) have shown great convenience for spectrally separating the molecule and aerosol scattering components in the high-spectral-resolution lidar (HSRL) returnsignal. In this paper, performance comparisons between the FPI and FWMI as a spectroscopic discrimination filter in HSRL are performed. We first present a theoretical method for spectral transmissionanalysis and quantitative evaluation on the spectral discrimination. Then the process in determiningthe parameters of the FPI and FWMI for the performance comparisons is described. The influences fromthe incident field of view (FOV), the cumulative wavefront error induced by practical imperfections, andthe frequency locking error on the spectral discrimination performance of the two filters are discussed indetail. Quantitative analyses demonstrate that FPI can produce higher transmittance while the remarkable spectral discrimination is one of the most appealing advantages of FWMI. As a result of the field-widened design, the FWMI still performs well even under the illumination with large FOV while the FPIis only qualified for a small incident angle. The cumulative wavefront error attaches a great effect on thespectral discrimination performance of the interferometric filters. We suggest if a cumulative wavefronterror is less than 0.05 waves RMS, it is beneficial to employ the FWMI; otherwise, FPI may be moreproper. Although the FWMI shows much more sensitivity to the frequency locking error, it can outperform the FPI given a locking error less than 0.1 GHz is achieved. In summary, the FWMI is very competent in HSRL applications if these practical engineering and control problems can be solved,theoretically. Some other estimations neglected in this paper can also be carried out through theanalytical method illustrated herein.
供稿:师途







