一、 本期重点:
1.基于全画幅光热反射显微镜的光学材料吸收型缺陷快速检测(Fast mapping of absorbing defects inoptical materials by full-fieldphotothermal reflectance microscopy)【OPTICS LETTERS】
DOI:10.1364/OL.38.004907
内容介绍:
韩国基础科学研究院的Woo June Choi等人提出了一种适用于可诱发激光损伤的光学材料的吸收型缺陷的快速定位方法。采用光强调制型的泵浦光源加热光学样品的吸收型缺陷,引起缺陷附近折射率场的变化。然后采用探测光束照明缺陷区域,检测体缺陷的分布情况。检测结果表明,这种方式提供了一种更加快速的缺陷定位技术,检测速度每分钟0.03mm2,检测分辨率达到几十纳米量级。
文章给出了系统的详细参数,并采用不同尺寸的化合物或金属模拟有缺陷的光学材料,将微米量级的检测结果与光学显微镜比对,证明了系统的可靠性;之后,纳米量级的检测结果表明系统能够检测到纳米量级的缺陷。最后,对真实的疵病进行检测,能够检测不同深度的缺陷。
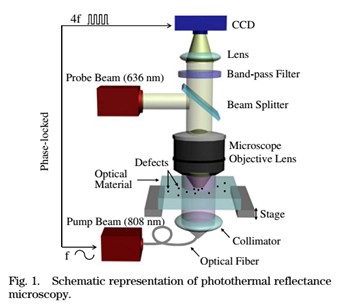
图1 光热反射显微镜系统原理图
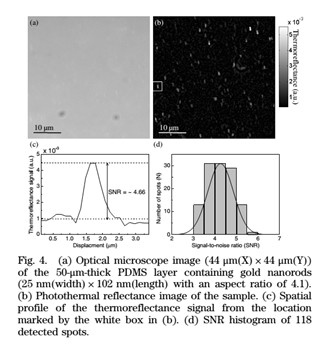
图4 光学显微镜和光热反射显微镜对同一样品所包含的纳米级缺陷
检测图像及信噪比
2.入射角和偏振态对融石英缺陷区域的影响(Influence of incidence angle and polarization state onthe damage site characteristics of fused silica)【APPLIED OPTICS】
DOI:10.1364/AO.53.000A96
内容介绍:
本文研究了采用355nm的激光照射融石英时,不同的入射角和偏振态对融石英缺陷区域的影响。将各种入射角和偏振态的入射光与入射角为0°和45°的入射光的原始的缺陷形貌和在出射面的缺陷生长状态进行比较。讨论了原始缺陷的尺寸、激光影响、增长阈值。接着研究了在不同的入射光和偏振态下的火山口缺陷和划痕的缺陷形貌。最后,比较了横向尺寸、火山口深度、划痕深度的增长尺寸特性,并进行了分析。
研究结果表明,典型的划痕有三种方向的延伸:沿着入射激光方向、与入射角成45°方向,因此划痕的结构不是完全对称的,此外,在0°时,侧向方向的增长系数略高,但是增长系数比45°在P光或S光状态下的更小。然而,P光和S光的状态下,增长系数没有发现差异。
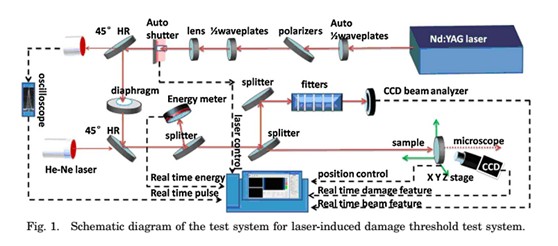
图1 激光诱导损伤阈值测试系统原理图
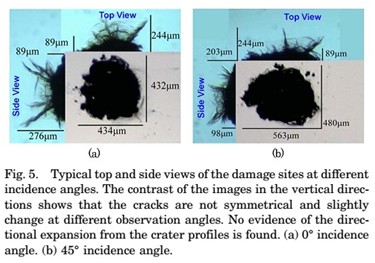
图5 在不同入射角下的缺陷区域正视图和侧视图
二、 简讯:
DOI:10.1364/AO.52.008117
published:2013.11.20
Abstract:
A dark-field imaging technique taking advantage of the active polymer slab waveguide (APSW) is experimentally investigated. The dye molecules (Rhodamine 6G, Rh6G) are doped in the polymer film for the launching of surface waves on the APSW, such as the surface plasmon polaritons on the Ag–polymer–air interface, evanescent fields at the polymer–air interface by the total internal reflection, or the guided modes. The localized surface waves will not radiate into the far-field space directly. When the specimens are placed on the surface of the APSW, these surface waves will be scattered to the far-field region, which forms the dark-field image of the specimen. Experimental results show that usage of APSW leads to high-contrast dark-field images with the conventional optical microscope system. The polymer film involved in the proposed dark-field microscopy brings about the merits of reduced roughness, good stability, bio-compatibility, and shorter wavelength of the illumination light source.
DOI:10.1364/OE.21.0A1113
Abstract:
Laser ignition (LI) has been shown to offer many potential benefits compared to spark ignition (SI) for improving the performance of internal combustion (IC) engines. This paper outlines progress made in recent research on laser ignited IC engines, discusses the potential advantages and control opportunities and considers the challenges faced and prospects for its future implementation. An experimental research effort has been underway at the University of Liverpool (UoL) to extend the stratified speed/load operating region of the gasoline direct injection (GDI) engine
through LI research, for which an overview of some of the approaches, testing and results to date are presented. These indicate how LI can be used to improve control of the engine for: leaner operation, reductions in emissions, lower idle speed and improved combustion stability.
DOI:10.1364/OE.21.026219
published:2013.11.04
Abstract:
Optical microscopy is sensitive both to arrays of nanoscale features and to their imperfections. Optimizing scattered electromagnetic field intensities from deep sub-wavelength nanometer scale structures represents an important element of optical metrology. Current, well-established optical methods used to identify defects in semiconductor patterning are in jeopardy by upcoming sub-20 nm device dimensions. A novel volumetric analysis for processing focus-resolved images of defects is presented using simulated and experimental examples. This new method allows defects as narrow as (16 ± 2) nm (k = 1) to be revealed using 193 nm light with focus and illumination conditions optimized for three-dimensional data analysis. Quantitative metrics to compare two-dimensional and three-dimensional imaging indicate possible fourfold improvements in sensitivity using these methods.
DOI:10.1364/OL.38.004510
published:2013.11.01
Abstract:
We implement switching laser mode coherent anti-Stokes Raman-scattering (SLAM-CARS) microscopy to enhance the spatial resolution and contrast in label-free vibrational microscopy. The method, based on the intensity difference between two images obtained with Gaussian and doughnut-shaped modes, does not depend on the specimen and relies on minimal modifications of the typical CARS setup. We demonstrate subdiffraction resolution imaging of myelin sheaths in a mouse brainstem. A lateral resolution of 0.36λp is achieved.
供稿:李璐







