一、本期重点:
doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2013.04.007
published:2013.6.4
文章展示了一种利用垂直腔面发射的激光光源的新型扫频OCT系统,能够用于全眼成像。利用此方法能够进行非接触的生物统计学测量。针对于眼内距离测量,文章还将扫频OCT和现有商用的基于光学和超声的其他类型仪器进行了一个比较,并评估了利用扫频OCT对于眼内距测量的可再现性。
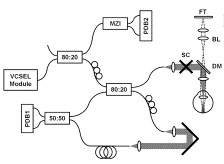
2.用扫频光源OCT和傅里叶域OCT进行啮齿类动物的活体眼成像( In vivo imaging of the rodent eye with swept source/Fourier domain OCT)【Optics Express】
doi: 10.1364/BOE.4.000351
published:2013.2.1
内容介绍:
文章介绍了一种OCT系统原型用来进行小动物的眼部成像。系统利用了1050nm的光源,轴向扫描速度达到100KHz,同时轴向分辨率约为6µm。快的成像速度使得很多工作成为可能。同时,相对于商用的光源中心波长在850nm的谱域OCT,1050nm在组织中的穿透能力更强。而大的成像深度能满足多种成像操作模式,如对视网膜、眼后节、眼前节以及全眼的成像。高速扫频OCT在对啮齿类动物的眼部成像很有应用的前景,它能提供综合性的眼部的各种信息。
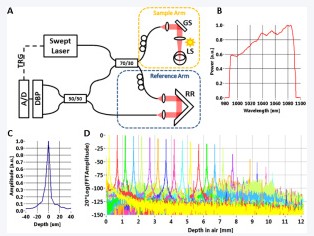
图二(A) 高速扫频/傅里叶OCT系统的原理图. (B) 光源光谱. (C) 点扩散函数显示轴向分辨率. (D)灵敏度下降图.
二、简讯:
doi:10.1364/OE.21.018021
published:2013.7.29
Abstract:
We demonstrate high speed, swept source optical coherence microscopy (OCM) using a MEMS tunable vertical cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL) light source. The light source had a sweep rate of 280 kHz, providing a bidirectional axial scan rate of 560 kHz. The sweep bandwidth was 117 nm centered at 1310 nm, corresponding to an axial resolution of 13.1 µm in air, corresponding to 8.1 µm (9.6 µm spectrally shaped) in tissue. Dispersion mismatch from different objectives was compensated numerically, enabling magnification and field of view to be easily changed. OCM images were acquired with transverse resolutions between 0.86 µm - 3.42 µm using interchangeable 40X, 20X and 10X objectives with ~600 µm x 600 µm, ~1 mm x 1 mm and ~2 mm x 2 mm field-of-view (FOV), respectively. Parasitic variations in path length with beam scanning were corrected numerically. These features enable swept source OCM to be integrated with a wide range of existing scanning microscopes. Large FOV mosaics were generated by serially acquiring adjacent overlapping microscopic fields and combining them in post-processing. Fresh human colon, thyroid and kidney specimens were imaged ex vivo and compared to matching histology sections, demonstrating the ability of OCM to image tissue specimens.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2013.06.01
published:2013.6.11
To investigate the appearance of postoperative spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SDOCT) and the relationship of the findings to visual acuity in myopic foveoschisis.
doi: 10.1364/OE.21.009757
published:2013.4.22
Abstract:
State-of-the-art Fourier-domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) allows for the acquisition of up to millions of spectral fringes per second. This large amount of data can be used to improve the quality of structural tomograms after effective averaging. Here, we compare three OCT image improvement techniques: magnitude averaging, complex averaging, and spectral and time domain OCT (STdOCT). We evaluate the performance for images on both linear and logarithmic intensity scales and discuss their advantages and disadvantages. We propose the use of the STdOCT approach as it offers the best advantages. Applications to in vivo imaging and speckle reduction are presented.
doi: 10.1364/OE.21.017711
published:2013.7.29
Abstract:
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) and optical coherence microscopy (OCM) allow the acquisition of quantitative three-dimensional axial flow by estimating the Doppler shift caused by moving scatterers. Measuring the velocity of red blood cells is currently the principal application of these methods. In many biological tissues, blood flow is often perpendicular to the optical axis, creating the need for a quantitative measurement of lateral flow. Previous work has shown that lateral flow can be measured from the Doppler bandwidth, albeit only for simplified optical systems. In this work, we present a generalized model to analyze the influence of relevant OCT/OCM system parameters such as light source spectrum, numerical aperture and beam geometry on the Doppler spectrum.Our analysis results in a general framework relating the mean and variance of the Doppler frequency to the axial and lateral flow velocity components.Based on this model, we present an optimized acquisition protocol and algorithm to reconstruct quantitative measurements of lateral and axial flow from the Doppler spectrum for any given OCT/OCM system. To validate this approach, Doppler spectrum analysis is employed to quantitatively measure flow in a capillary with both extended focus OCM and OCT.
供稿人:倪秧







