一、本期重点:
1.适用于量子信息处理的多功能单光子源(A versatile source of single photons for quantum information processing)[Nature. Communication]
doi: 10.1038/ncomms2838
published: 2013.05.07
内容介绍:
在诸如量子通信,量子信息处理,量子测量这些基础科学和应用的研究中,如何有效地促进原子系统与非经典光场的耦合是一个不可回避的问题。在这个问题上,产生带宽可控、中心波长可调的窄带高质量单光子光源非常关键。
本文用铌酸锂制成单片微盘形成回音壁模式谐振腔(WGMR),利用腔辅助的自发下转换过程(SPDC),产生了带宽/中心波长均可调谐、窄带、高效的单光子源。调节微腔的温度和电压,中心波长调谐范围可达100nm;调节微腔与耦合棱镜之间的距离,带宽可在7.2MHz到13MHz之间调节;在宣布式单光子源的反聚束效应测量中,g(2)(0)<0.2。将本文的结构放置在Sagnac环中,还将可以产生偏振量子纠缠源。
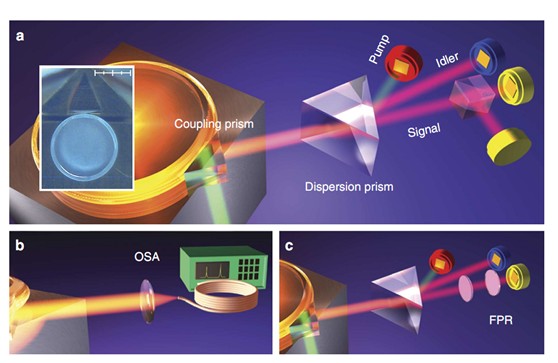
图1 利用微腔辅助的自发下转换产生单光子源
2.衬底支撑的银纳米线中表面等离子的调制(Highly tunable propagating surface plasmons on supported silver nanowires)[PNAS.]
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1217931110
published: 2013. 03. 19
内容介绍:
表面等离子是由金属表面自由电子的集群振荡产生,可以通过改变介质环境来实现对表面等离子的调控。
本文报道了一种有效调制表面等离子的方法。通过改变金属银纳米线表面涂敷层(Al2O3)的厚度或者外界介质材料的折射率,来改变等离子拍的周期以及近场分布,从而实现对表面等离子的调控。实验中,氧化铝涂层的厚度每增加1 nm,等离子拍的周期随之增加90 nm; 外界折射率每变化1RIU(refractive index unit),等离子拍的周期随之增加16 μm。这种有效的调制方法在超灵敏传感检测和全光网络构建等方面具有潜在的应用前景。
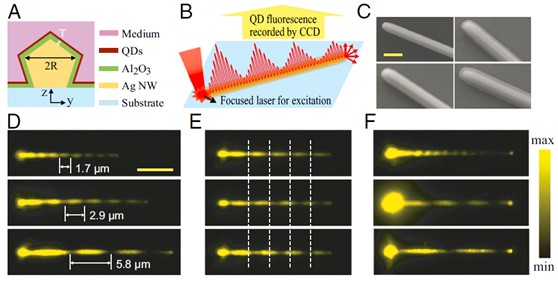
图2 银纳米线中表面等离子拍的在不同介质环境下的情况
二、简讯:
doi:10.1038/nature11573
published:2012.11.14
Entanglement has a central role in fundamental tests of quantumMechanicsas well as in the burgeoning fieldof quantuminformation processing. Particularly in the context of quantum networksand communication, amain challenge is the efficient generation ofentanglement between stationary (spin) and propagating (photon)quantum bits. Here we report the observation of quantum entanglement between a semiconductor quantum dot spin and the
colour of a propagating optical photon.
2.石墨烯中狄拉克费米子飞秒尺度上的粒子数反转和受激辐射研究(FemtosecondPopulation Inversion and Stimulated Emissionof Dense Dirac Fermions in Graphene)
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.167401
published:2012.04.16
Abstract:
We show that strongly photoexcitedgraphene monolayers with 35 fs pulses quasi-instantaneously buildup a broadband, inverted Dirac fermion population. Optical gain emerges and directly manifests itself viaa negative conductivity at the near-infrared region for the first 200 fs, where stimulated emissioncompletely compensates absorption loss in the graphene layer. Our experiment-theory comparison withtwo distinct electron and hole chemical potentials reproduce absorption saturation and gain at 40 fs,revealing, particularly, the evolution of the transient state from a hot classical gas to a dense quantum fluidwith increasing the photoexcitation.
doi:10.1038/NPHYS2748
published:2013.09.15
Abstract:
A variety of nanomechanical systems can now operate atthe quantum limit, making quantum phenomena more accessible for applications and providing new opportunitiesfor exploring the fundamentals of quantum physics. Suchmechanical quantum devices offer compelling opportunitiesfor quantum-enhanced sensing and quantum information. Furthermore, mechanical modes provide a versatile quantum bus for coupling hybrid quantum systems, supportinga quantum-coherent connection between different physicaldegrees of freedom. Here, we demonstrate a nanomechanical interface between optical photons and microwave electrical signals, using a piezoelectric optomechanical crystal.
doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.123602
published:2013.09.20
Abstract:
We observe narrow band pairs of time-correlated photons of wavelengths 776 and 795 nm from nondegenerate four-wave mixing in a laser-cooled atomic ensemble of87Rb using a cascade decayscheme. Coupling the photon pairs into single mode fibers, we observe an instantaneous rate of 7700 pairsper second with silicon avalanche photodetectors, and an optical bandwidth below 30 MHz. Detectionevents exhibit a strong correlation in time [g(2)(τ=0)≈ 5800] and a high coupling efficiency indicatedby a pair-to-single ratio of 23%. The violation of the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality by a factor of 8.4*106 indicates a strong nonclassical correlation between the generated fields, while a Hanbury Brown–Twissexperiment in the individual photons reveals their thermal nature. The comparison between the measuredfrequency bandwidth and 1/e decay time ofg(2)indicates a transform-limited spectrum of the photon pairs. The narrow bandwidth and brightness of our source makes it ideal for interacting with atomicensembles in quantum communication protocols.
供稿人:徐颖鑫、王一霈、林星、虞绍良







